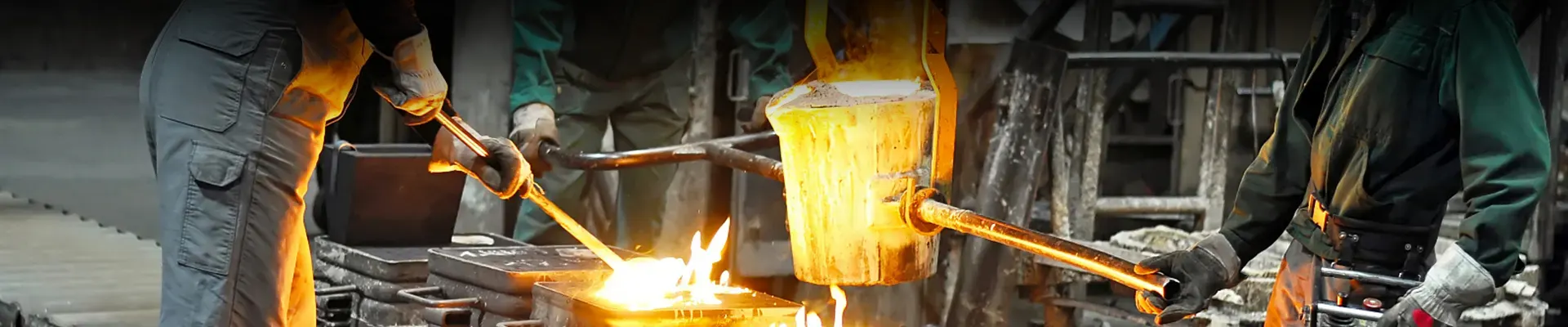- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
China Gray Iron Casting Factory
Gray cast iron refers to cast iron with flake graphite. It is called gray cast iron because the fracture surface is dark gray when it breaks.
1.Performance characteristics of Gray Iron Casting
The mechanical properties of gray cast iron are related to the structure of the matrix and the morphology of graphite. The flake graphite in gray cast iron seriously cuts the matrix, which easily causes stress concentration at the sharp corners of graphite, making the tensile strength, plasticity and toughness of gray cast iron far lower than that of steel, but the compressive strength is equivalent to that of steel. It is also the cast iron with the worst mechanical properties among commonly used cast iron parts. At the same time, the matrix structure also has a certain influence on the mechanical properties of gray cast iron. The graphite flakes of ferrite-based gray cast iron are coarse, with the lowest strength and hardness, so it is less used; the graphite flakes of pearlite-based gray cast iron are fine, with higher strength and hardness, and are mainly used to manufacture more important castings; the graphite flakes of ferrite-pearlite-based gray cast iron are slightly coarser than pearlite gray cast iron, and the performance is not as good as pearlite gray cast iron. Therefore, pearlite-based gray cast iron is more commonly used in industry.
Gray cast iron has good casting performance, good vibration damping, good wear resistance, good cutting performance and low notch sensitivity.
|
Table: Grades and mechanical properties of gray iron castings |
|||||
|
Brand |
Casting wall thickness |
Minimum tensile strength |
Hardness classification |
Casting hardness range |
Main metallographic structures |
|
HT100 |
2.5~10 |
130 |
H145 |
≤170 |
Ferrite |
|
10~20 |
100 |
||||
|
20~30 |
90 |
||||
|
30~50 |
80 |
||||
|
HT150 |
2.5~10 |
175 |
H175 |
150~200 |
Ferrite +Pearlite
|
|
10~20 |
145 |
||||
|
20~30 |
130 |
||||
|
30~50 |
120 |
||||
|
HT200 |
2.5~10 |
220 |
H195 |
170~220 |
Pearlite |
|
10~20 |
195 |
||||
|
20~30 |
170 |
||||
|
30~50 |
160 |
||||
|
HT250 |
4.0~10 |
270 |
H215 |
190~240 |
Pearlite |
|
10~20 |
240 |
||||
|
20~30 |
220 |
||||
|
30~50 |
200 |
||||
|
HT300 |
10~20 |
290 |
H235 |
210~260 |
100% pearlite
(nodular cast iron)
|
|
20~30 |
250 |
||||
|
30~50 |
230 |
||||
|
HT350 |
10~20 |
340 |
H255 |
230~280 |
100% pearlite
(nodular cast iron)
|
|
20~30 |
290 |
||||
|
30~50 |
260 |
||||
2、Chemical composition of grey cast iron
|
National standard chemical composition of grey cast iron (%) |
|||||
|
Ingredients Standard
|
C |
S |
Mn |
P |
Si |
|
HT100 |
3.2~3.8 |
≤0.15 |
0.5~0.8 |
<0.3 |
2.1~2.7 |
|
HT150 |
3.0~3.7 |
≤0.12 |
0.5~0.8 |
<0.2 |
1.8~2.4 |
|
HT200 |
3.0~3.6 |
≤0.12 |
0.6~1.0 |
<0.15 |
1.4~2.2 |
|
HT250 |
2.9~3.5 |
≤0.12 |
0.7~1.1 |
<0.15 |
1.2~2.0 |
|
HT300 |
2.8~3.4 |
≤0.12 |
0.8~1.2 |
<0.15 |
|
|
HT350 |
2.7~3.2 |
≤0.12 |
0.8~1.4 |
<0.15 |
|
3、Comparison of Chinese and foreign grades of grey cast iron
|
Serial number |
Country |
Cast iron grade |
||||||
|
1 |
China |
|
HT350 |
HT300 |
HT250 |
HT200 |
HT150 |
HT100 |
|
2 |
Japan |
|
FC350 |
FC300 |
FC250 |
FC200 |
FC150 |
FC100 |
|
3 |
United States |
NO.60 |
NO.50 |
NO.45 |
NO.35 |
N0.30 |
NO.20 |
|
|
4 |
Former Soviet Union |
C440 |
C435 |
C430 |
C425 |
C420 |
C415 |
C410 |
|
5 |
Germany |
GG40 |
GG35 |
GG30 |
GG25 |
GG20 |
GG15 |
|
|
6 |
Italy |
|
G35 |
G30 |
G25 |
G20 |
G15 |
G10 |
|
7 |
France |
FGL400 |
FGL350 |
FGL300 |
FGL250 |
FGL200 |
FGL150 |
|
|
8 |
United Kingdom |
|
350 |
300 |
250 |
200 |
150 |
100 |
|
9 |
Poland |
Z140 |
Z135 |
Z130 |
Z125 |
Z120 |
Z115 |
|
|
10 |
India |
FG400 |
FG350 |
FG300 |
FG260 |
FG200 |
FG150 |
|
|
11 |
Romania |
FC400 |
FC350 |
FC300 |
FC250 |
FC200 |
FC150 |
|
|
12 |
Spain |
|
FG35 |
FG30 |
FG25 |
FG20 |
FG15 |
|
|
13 |
Belgium |
FGG40 |
FGG35 |
FGG30 |
FGG25 |
FGG20 |
FGG15 |
FGG10 |
|
14 |
Australia |
T400 |
T350 |
T300 |
T260 |
T220 |
T150 |
|
|
15 |
Sweden |
0140 |
0135 |
0130 |
0125 |
0120 |
0115 |
0110 |
|
16 |
Hungary |
OV40 |
OV35 |
OV30 |
OV25 |
OV20 |
OV15 |
|
|
17 |
Bulgaria |
|
Vch35 |
Vch30 |
Vch25 |
Vch20 |
Vch15 |
|
|
18 |
International Standard (IS0) |
|
350 |
300 |
250 |
200 |
150 |
100 |
|
19 |
Pan-American Standard (COPANT) |
FG400 |
FG350 |
FG300 |
FG250 |
FG200 |
FG150 |
FG100 |
|
20 |
Taiwan, China |
|
|
FC300 |
FC250 |
FC200 |
FC150 |
FC100 |
|
21 |
Netherlands |
|
GG35 |
GG30 |
GG25 |
GG20 |
GG15 |
|
|
22 |
Luxembourg |
FGG40 |
FGG35 |
FGG30 |
FGG25 |
FGG20 |
FGG15 |
|
|
23 |
Austria |
|
GG35 |
GG30 |
GG25 |
GG20 |
GG15 |
|
4、Application areas of grey cast iron
1) Ferritic gray cast iron, grade HT100, is suitable for unimportant castings with small loads and no special requirements for friction and wear, such as protective covers, covers, oil pans, handwheels, brackets, base plates, heavy hammers, small handles, etc.
2) Ferritic-pearlitic gray cast iron, grade HT150, is suitable for castings with medium loads, such as machine bases, brackets, boxes, tool holders, bed bodies, bearing seats, workbenches, pulleys, end covers, pump bodies, valve bodies, pipelines, flywheels, motor bases, etc.
3) Pearlitic gray cast iron, grade HT250, is suitable for more important castings that bear larger loads and require certain air tightness or corrosion resistance, such as cylinders, gears, machine bases, flywheels, bed bodies, cylinder blocks, cylinder liners, pistons, gear boxes, brake wheels, coupling discs, medium pressure valve bodies, etc.
4) Nodular cast iron, with grades HT300 and HT350, is used for important castings that require high load, wear resistance and high air tightness, such as the bed, base and frame of heavy machine tools, shearing machines, presses and automatic lathes, high-pressure hydraulic parts, piston rings, gears, cams and bushings with large forces, crankshafts, cylinder blocks, cylinder liners and cylinder heads of large engines, etc.
- View as